Search for articles or browse our knowledge portal by topic.
Section Engineer
Section Engineers (SE) oversee construction and maintenance projects across multiple counties. Their position is one that is highly visible to the public and stakeholders, and therefore is quite demanding. SEs are responsible for administering construction projects, planning maintenance work, supervising maintenance crews, and collaborating with many stakeholders, including:
-
- Central Office (CO), District Office (DO), and other Section Engineer Offices at the Cabinet
- Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) staff
- Public
- Politicians
- Federal Emergency Management Administration (FEMA) staff
- Utility Companies
- Public Information Officer (District)
- Emergency management agencies (when necessary)
- Contractors
- Local Agencies/governments
- Consultant Engineering Firms
- Kentucky Transportation Center
SEs must be careful and attentive planners. Proper planning is critical for having adequate resources to manage ongoing and impending jobs/projects.
Construction work largely depends on contractors and their schedules. Staffing can become a challenge if a crew has many active projects. If not enough KYTC staff are available to perform inspections, it may become necessary to rely on consultant inspection. The SE must have good communication with their own staff and contractors. Demands can change quickly, and the SE must be flexible.
Maintenance projects vary in terms of their priority. For example, the SE has routine, day-to-day projects they will plan to work on. However, emergency or high-priority projects can arise whose importance and urgency supersedes routine project work. The SE must coordinate work on unexpected projects to fit in with their planned work. SEs are also involved in planning and organizing maintenance projects that will be scheduled in the upcoming season. When planning for and selecting upcoming projects, the SE must weigh needs against available funding.


Early AM (prior to Dispatching Crews)
Review new emails
-
-
Based on the volume of emails, their respective lengths, and the amount of time the SE can dedicate, they may completely review and respond to each email or quickly review senders and subjects to determine which are most urgent
-
Check whether contractor(s) have reached out to address the following:
-
- Emergence of previously unknown issues
- Proposals to amend plans
Contact KYTC’s Central Office to obtain needed material or information such as completed inspection reports, to schedule inspections, or information from other Divisions in Central Office.
Check in with inspectors to review the previous day’s work and work scheduled for the upcoming day
Review and discuss concerns voiced by inspectors. Help inspectors prioritize their time by discussing critical work items to address during the upcoming day.
-
- Check in with maintenance crews to review work from the day before and the workplan for the upcoming day
- Determine what methods are needed to carry out maintenance projects (i.e., slides, pavement patches, bridge repairs) using either KYTC forces or master agreements for external vendors.
- When using KYTC forces, secure equipment and materials using purchase orders.
- When using master agreements, issue delivery orders and ensure work is completed in accordance with the terms of the agreement.
Verify that tickets match submitted invoices
Coordinate with District Office contact (this person may differ from district to district) so county inmate crews can complete maintenance tasks such as trash pickup, mowing, and weed trimming. Assign resources to monitor work.
-
- Establish mowing schedule for contract county mowing. Monitor work during the mowing cycle
Schedule urgent work items, if any have arisen.
NOTE: Depending on crew personnel (i.e., staff engineers on the crew), the SE may coordinate current work with and disseminate information to those persons who will disseminate to the crew. Otherwise, the SE will then develop assignments and discuss them with crews at the beginning of the day.
Available resources: Standard Specifications, Standard Drawings, Construction and Maintenance Guidance Manuals
Mid-AM (Following Crew Dispatch)
Review daily timesheets for Section Office and maintenance crews
-
- Verify that the correct project charges, equipment, and materials are reported (OMS data)
- Verify that correct shift premium hours are reported (Highway Technicians)
- Approve timesheets after verifying all information is correct
Review daily work reports (DWRs) for construction projects
-
- Review documented work
- Review pay items
- Verify that drawings or sketches that further explain or detail work are attached
- Verify that calculations are attached and accurate
- Review scanned items (e.g., material tickets)
- Prior to remitting payment for materials, verify that inspectors have obtained certification or a sample
- Approve DWRs after verifying all information is correct
- Review Contractor personnel and equipment.
Review and approve material samples assigned to the Section Office
Visit projects
-
- Activities for all projects—Check with inspectors on:
- Safety
- Inspectors
- Contractors
- Traffic Control
- Erosion Control
- Materials sampling and testing
- Surveying/staking need
Activities for resurfacing projects—Check with inspectors on:
-
- Yield. Inspectors should calculate theoretical tonnage based on depth placed and area paved, and compare to the actual tonnage placed
- Temperature (ambient and mix)
- Cores
- Haul routes to identify areas of concern (e.g., busy intersections, bridge ratings, narrow routes, interstate weight restrictions)
- Tack application rate
Activities for grade projects—Check with inspector on:
-
- Proper placement of fill — lifts and material
- Cuts are accurately located according to plans
-
Verify that the offset of the cut stakes matches the offsets shown in cross sections. Verify the cut is within template
-
-
Proper drainage structures (pipes and culverts)
-
Densities and proctors are being performed
Activities for bridge projects
-
- Check staking and review contractor surveying
- Verify elevation shots are taken as needed
- Check scheduling, especially for beam and deck placement
-
Discuss traffic control for delivery
-
Schedule pre-pour meetings. Topics of discussion at meetings include:
-
Access routes
-
Staging areas
-
Pump truck location
-
Confirm that inspectors have appropriate testing items (e.g., air meter, slump cone, cylinder molds)
Develop and submit piling reports to Branch Manager for approval
Verify piles are in correct position and/or orientation
Upcoming projects
Verify necessary surveying and/or staking is done
Address issues/areas that arose during the day (e.g., Chief District Engineer called about an area that needs tobe addressed; local residents or politicians raised concerns about an issue)
-
- Maintenance projects
- Verify proper traffic control
-
Check location and spacing of signs and flaggers
-
Verify appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is in use
-
Verify the use of proper materials and methods
-

Draft memos requesting the following personnel actions:
-
- New hires
- Promotions
- Reclassifications
- Disciplinary actions
Staff meetings
-
- Policy changes
- Safety
- Confirm all staff are current on training and certifications
- Upcoming projects and inspection assignments
Maintain office and equipment
-
- Verify office is clean and maintained
- This provides a healthy and safe work environment for staff while in the office
- Perform routine vehicle checks (e.g., motor oil, tire air pressure)
- Schedule routine maintenance for trucks
- Report equipment damage in accordance with Cabinet policy
- For equipment maintenance and repairs, coordinate with district mechanic which may be assigned to the district or a specific SE crew, depending on the district.
- Verify office is clean and maintained
Request (as necessary) access to available equipment:
-
- Trucks
- Testing equipment
- iPads
- Office supplies
- Computers
- PPE
Verify Procards are issued to appropriate staff and adherence to policy
-
- Establish office policy within KYTC guidelines for Procard usage (i.e. purchase approval process)
- Confirm the charge amount matches the amount listed on the receipt and tax exemption is applied
- Identify the account that Procard charge is assigned to
- Determine the activity code for the Procard charge
Maintenance Rating Program Review
Participate on Design Project team
Complete employee performance report for subordinates
On call and/or work District Office Operations room for weather events
Review final construction project packages for completeness. Submit packages once they have been reviewed.
Conduct Pre-Construction and Pre-Pave meetings prior to projects beginning
Maintenance Duties
- Maintenance purchases
- Review previous purchases
- Submit new purchases as needed and/or requested purchases
-
Equipment Issues
-
Schedule shared equipment (e.g., ditching equipment, slope mower, roller, spray truck)
-
Work with Branch Manager and Equipment Supervisor on new equipment purchases and the equipment replacement schedule
-
-
CB06, FD05, Flood Repair for FEMA / FHWA, Guardrail and Various estimates
-
Collect field data
-
Double check quantities and notes before submitting to Central Office Maintenance
-
-
Select routes for routine maintenance (primarily resurfacing)
-
Identify projects for the upcoming year based on the county budget. This is commonly done with the county foreman’s input.
-
Present budget and selected projects at the Fiscal Court meeting
-
-
Develop and provide direction of Maintenance of Traffic (MOT) on Cabinet maintenance projects
-
Work with the Office of Highway Safety Improvement Program (HSIP) to identify areas that qualify for funding to improve roadway safety
-
Review encroachment permits and submit comments to District Office
-
Prepare guardrail inventory
-
Select candidate road segments for guardrail installation via the Guardrail program to prioritize candidates for available funding.
-
Choose locations that meet the warrants for guardrail based upon the Roadside Design Guide. Input location criteria into the Guardrail program. The program assigns a weighted score based upon need. Then, the need will be addressed based on available funding for a one- or two-year cycle. After a project is selected, the SE will assemble a proposal so the project can be let and eventually constructed.
-
- Complete quarterly materials inventory
-
Inventory of stockpiled material on maintenance lots
-
-
Complete quarterly environmental inspections for maintenance lots
-
Support the Chief District Engineer (CDE) in assessing, accounting, and tracking budgets for each county
-
Develop a yearly plan for allocating resources to meet the needs in each county. This requires continuously monitoring for unknown or changing circumstances
-
For snow and ice events:
- Verify trucks are on priority routes
- Coordinate state forces and contract trucks
-
Inspect contract trucks
-
Attend safety meeting for contract truck drivers
-
-
Check salt usage and calcium usage.
-
Maintain inventory of snow and ice materials

KYTC’s Divisions use different conventions to identify projects:
- Construction and Construction Procurement—Assigns a six-digit CID number to a project when it is scheduled in a letting. The first two digits (YY) are the year of the letting. The next two digits (**) are based on what office is preparing the project. The last two digits are sequential numbers assigned as they prepared from the specific office.
-
CID-First 2 digits
-
YY—year let
-
CID-Digits 3 and 4
-
10, 11, 12, 13—Prepared and input by Highway Design
-
20, 21, 22—Maintenance
-
26, 27—Bridge maintenance
-
30, 31, 32—Rural Roads
-
40, 41, 42—HSIP
-
50, 51—Bridging KY
-

-
Maintenance—Uses roadway milepoints which can be found here: https://transportation.ky.gov/Planning/Pages/Centerlines.aspx
-
Structural Design—Uses structure numbers which can be found here: https://maps.kytc.ky.gov/bridgedataminer/ Or http://datamart.
-
Highway Design—Uses an item number—##-#####.##. The first two digits denote the district. The next five digits are based on the following table. The last 2 digits are usually 00, but may be sequential if other projects on the route are set up.
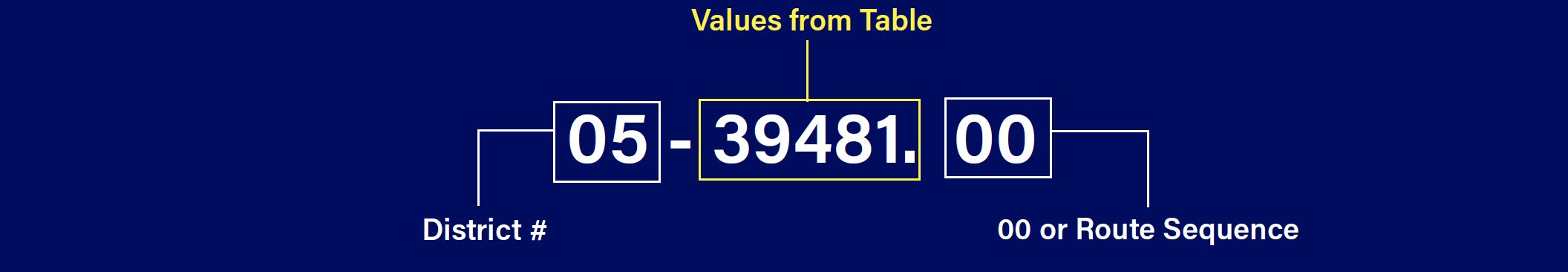

| Explanation of Item Number Series | |
|---|---|
| 900 - 999 | HES Projects |
| 1000 - 1999 | Federal Bridge Replacement Program |
| 2000 - 2999 | Pavement Rehabilitation (Interstate, Parkways or Primary Routes) |
| 3000 - 3199 | Transportation Enhancement Projects |
| 3200 - 3999 | ARRA MPO Dedicated Projects |
| 4000 - 4299 | County Bridge Replacement Program (State Funds) |
| 4300 - 4699 | Guardrail Replacement Program (State Funds) |
| 4700 - 4999 | School Turn Lane Projects |
| 5000 - 5999 | Rockfall and Landslide Repairs |
| 6000 - 6999 | Open |
| 7000 - 7999 | 1998 SYP General Assembly Added Projects |
| 8000 - 8099 | 2000 SYP General Assembly Added Projects |
| 8100 - 8199 | 2002 SYP General Assembly Added Projects |
| 8200 - 8299 | 2004 SYP General Assembly Added Projects |
| 8300 - 8399 | 2006 SYP General Assembly Added Projects |
| 8400 - 8599 | 2008 SYP General Assembly Added Projects |
| 8600 - 8699 | 2010 SYP General Assembly Added Projects |
| 8700 - 8799 | 2012 SYP General Assembly Added Projects |
| 8800 - 8899 | 2014 SYP General Assembly Added Projects |
| 8900 - 8999 | 2016 SYP General Assembly Added Projects |
| 9000 9999 | HSIP Projects |
| 10000 - 19999 | Bridge Program Projects |
| 20000 - 29999 | Pavement Management Projects |
| 80000 - 89999 | 2018 SYP General Assembly Added Projects |

