Knowledge Book – Project Management Guidebook (PMGB)

1.0) PMGB Introduction
KYTC’s Project Management Guidebook (PMGB) defines a common approach for application of project management techniques that can be applied to all KYTC highway projects through the project development process – which is normally the preconstruction stage of a project from the planning report to the project letting. Effective management is achieved by combining Project Management tools/techniques with sound application of project management principles. Key topics addressed in the guidebook will include assembling and developing a project team, improving management of project development, judicious oversight of project budgets, the relationship between individual projects and delivering KYTC’s program, and common obstacles that arise during project development. Practical guidance on addressing these challenges will also be provided.
An understanding of the interrelationship between scope, quality, schedule, and budget is fundamental to an understanding of what project management is. These three elements form the sides of a triangle and as in any triangular relationship a change in any element will result in a change in the other two sides.
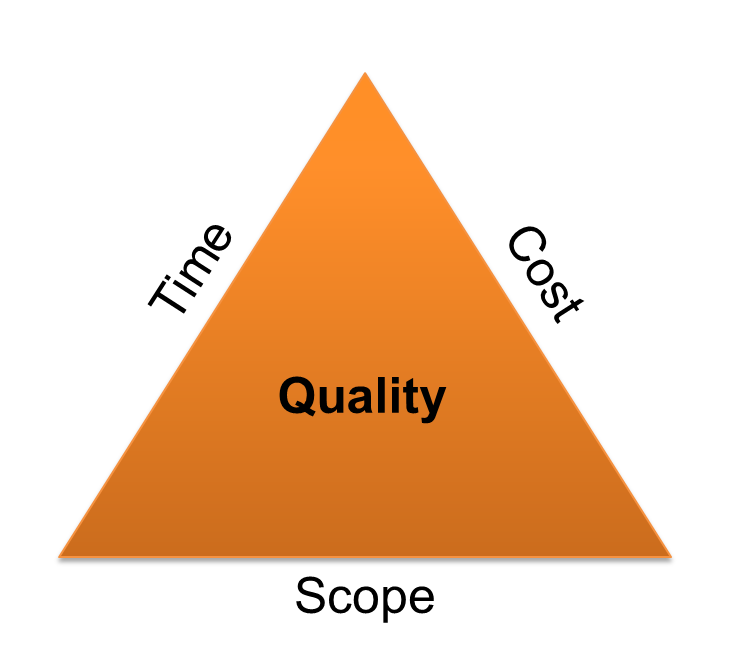

A change in the scope may impact budget and schedule. A reduced budget will impact scope and quality. A reduced delivery timeline may result in increased cost and possibly reduced quality and scope changes.
The definition of a successful project would be:
-
meets the defined scope
-
with quality solutions and deliverables
-
on schedule
-
within budget
Throughout project development, program and project managers should be mindful that every project is a promise and has a constituency. Adhering to the above principles helps to ensure that public and Cabinet expectations are met.
2.0) Project Management at KYTC
Project management at KYTC may differ significantly based on project type and complexity. Projects range from small, proposal only (no plans) projects with short durations to very complex projects with a full set of construction plans that may take multiple construction seasons to complete. The tasks described in the guidebook may not apply to all projects or may be simplified depending on the complexity and the impacts.
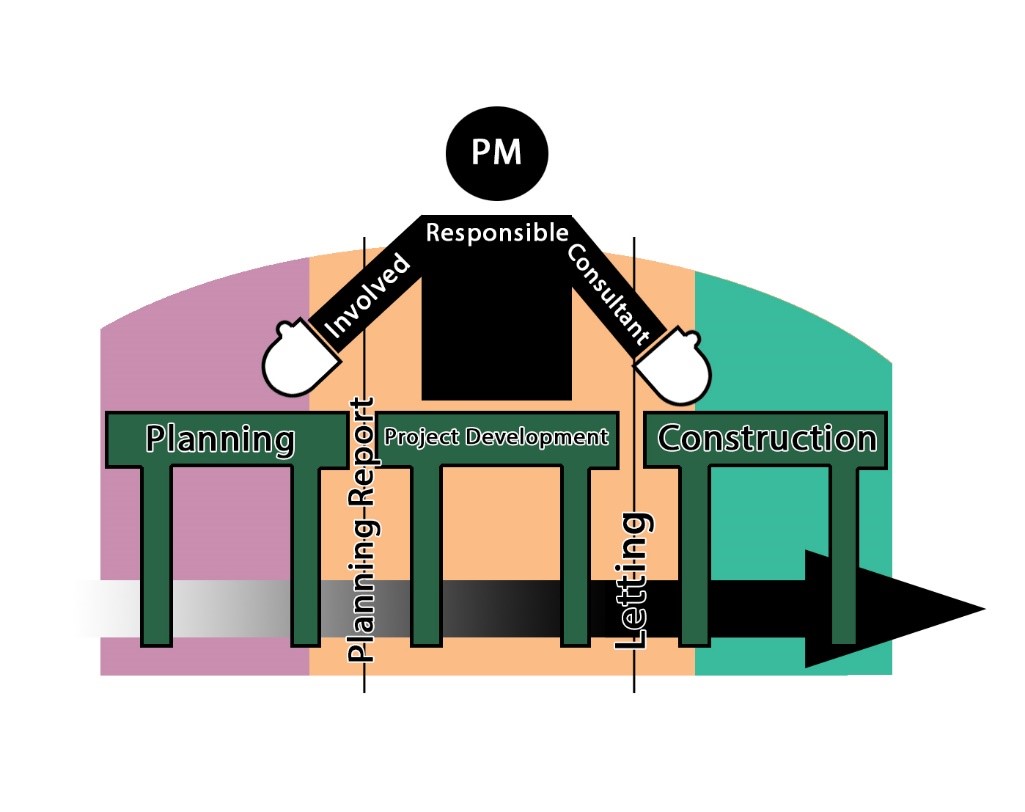
For the purposes of this guidebook, KYTC projects are grouped into the following four classifications:
-
Capital Improvement Projects – Projects with larger budgets that usually involve new road or bridge construction or major improvements to higher-traffic routes. They are included in the Highway Improvement Projects Listing in the current Highway Plan.
Safety Projects – Projects included in the Highway Safety Improvement Program (HSIP) that focus on reducing traffic fatalities and serious injuries on public roads. They are funded programmatically through federal funds designated for the HSIP.


-
Asset Management Projects – The primary purpose of these projects is to address the condition of existing highway assets through replacement or repair. They do not typically involve the addition of new capacity or roadway functionality, although minor improvements may sometimes be included. The most common asset management projects are those meant to address pavements or bridges that have deteriorated due to age and traffic impacts. They are included in the Existing Highway System Performance Projects Listing in the current Highway Plan. Examples include pavement resurfacing, bridge replacements, and pavement and bridge preventative maintenance and rehabilitation projects.
-
Maintenance Projects – Smaller scale projects that address the condition of existing highway assets, and do not involve the addition of new capacity or roadway functionality. They typically involve the restoration or repair of minor assets that contribute to the overall functionality of the roadway. If they are included in the Highway Plan, they are in the Existing Highway System Performance Projects Listing. Examples include re-striping of pavements, ditch cleaning, pothole patching, guardrail replacement, and minor bridge deck repairs.

Other project management guidance may exist for certain types of projects. One type of Alternative Delivery Project is design-build. Usually, design-build projects are developed through preliminary design as new or reconstruction projects; much of the guidance in this book will apply to these projects. For guidance specific to managing design-build projects, consult KYTC’s Design Build Guidance. Also, project managers for Local Public Agency (LPA) project administered through KYTC should consult KYTC’s LPA Guide.
3.0) PMGB Related Articles
The main purpose of the KYTC PMGB is to provide an easy-to-use overview of situations that might be encountered during the management of a highway project. For each of these topics, best practices, deliverables, pro tips, and potential red flags will be discussed as applicable.
The guidebook includes information on the following topics:
(Click underlined title below to navigate to each article)
-
Understanding the KYTC Budget and Highway Plan Process
-
Project Identification
-
Project Initiation
-
Project Scoping
-
Project Schedule & Development of Milestones
-
Project Cost Estimation and Management
-
Assembling a Project Development Team
-
Administration of Consultant Management – visit the Consultant Contract Management knowledge book page here, or see below)
-
Organizing and Running Effective Project Development Meetings
-
Common Project Team Meetings
-
Effective Communication in Project Management
-
Project Management & Planning
-
Project Management & NEPA
-
Project Management & Preliminary Design
-
Project Management & Final Design
-
Project Management & Right-of-Way Process
-
Project Management & Involvement in the Condemnation Process
-
Project Management & Utility Coordination
-
Project Management & Railroad Coordination
-
Managing Project Risk
-
Monitoring Scope, Budget, & Schedule
-
Public Involvement with Customers and Stakeholders
-
Preparing for Letting
-
Document Management, Storage, and Archival
-
Tools for the Project Manager
-
Project Management Training
Consultant Contract Management Guidebook Article (visit the knowledge book page here)
4.0) Information by Project Classification
Since the guidebook is a comprehensive Project Management Guidebook for a variety of project types, the information it contains may apply to one project classification or to a set or classifications. An effort is made throughout the guidance to identify when project management topics are commonly applicable based on project classification. Reference the table, like the one below, at the beginning of each article for applicable classifications.
| Knowledge Article | Project Classification | |||
| Capital Improvement Projects | Safety Projects | Asset Management Projects | Maintenance Projects | |
| 1.0 Topic 1 | x | x | x | x |
| 2.0 Topic 2 | x | x | x | |
| 3.0 Topic 2 | x | x | x | x |
|
3.1 Subtopic |
x | x | x | |
| 4.0 Topic 4 | x | x | x | |
| 4.1 Subtopic | x | x | x | |
| 4.2 Subtopic | x | x | x | |
| 4.3 Subtopic | x | x | x | |
| x = Information from the topic may be applicable for the project classification. | ||||

